9 Worst Supplements for Weight Loss

Let’s be honest: We all want the easiest solution when it comes to shedding pounds. As a result, many of us turn to weight-loss supplements in hopes of a quick fix. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) report that individuals in the U.S. spend a staggering $2.1 billion each year on weight-loss supplements, and roughly 15% of U.S. adults have taken a supplement for weight loss. However, not all supplements are created equal, and some may even do more harm than good. That’s why we chatted with registered dietitians and weight-loss experts who reveal the 10 worst supplements for weight loss to help you make informed choices on your journey to a slimmer, healthier you.
Destini Moody, RDN, CSSD, LD, a registered dietitian and sports dietitian with Garage Gym Reviews, tells ETNT, “The biggest problem with weight-loss supplements is they can create reliance. Taking a weight-loss supplement doesn’t teach you how to eat better or exercise more efficiently to maintain whatever weight it is that you lose. So, whether you’re taking the best or the worst weight-loss supplements, they should serve only to support your weight-loss goals, not be the cornerstone of your weight management efforts.”
While some supplements for weight loss promise miraculous results, they may contain harmful ingredients or have little scientific evidence to support their claims. Read on to discover the worst supplements for weight loss you should avoid, according to registered dietitians. Then, be sure to check out The #1 Best Type of Exercise for Weight Loss,
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)

Often marketed as a fat burner, CLA is a fatty acid found in dairy and meat products. While some studies suggest it may support weight loss, the evidence is mixed, and long-term effects are still unknown.
“Despite being widely known as a weight-loss supplement, studies have shown it has a wide range of effects on people who take it,” says Moody. “CLA may help you lose body fat, have no effect, or gain body fat. CLA’s effects seem to differ depending on who you are, but it’s not guaranteed to help you lose weight.”
Green Coffee Bean Extract

“Although green coffee bean extract contains chlorogenic acid, which is believed to help with weight loss, research findings are inconsistent,” explains Trista Best, RD, a registered dietitian with Balance One Supplements. “Additionally, the caffeine content in these supplements can cause side effects like jitteriness and increased heart rate.”
According to the NIH, green coffee bean extract supplements may also cause side effects like headaches and urinary tract infections.
Garcinia Cambogia
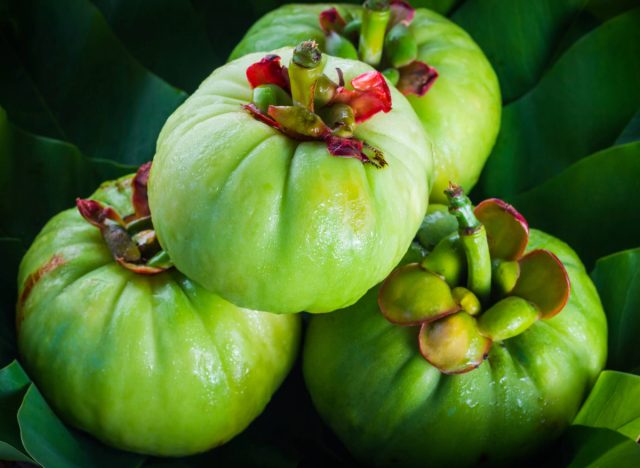

Garcinia cambogia is a tropical fruit touted for its potential weight-loss benefits. However, the research on its effectiveness is inconclusive.
“Garcinia cambogia was a main ingredient in Hydroxycut, a popular weight-loss supplement in 2009. However, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration advised against products that included this ingredient due to reports of liver damage. So, not only is this compound likely ineffective, but it could also be dangerous,” says Moody.
Hoodia
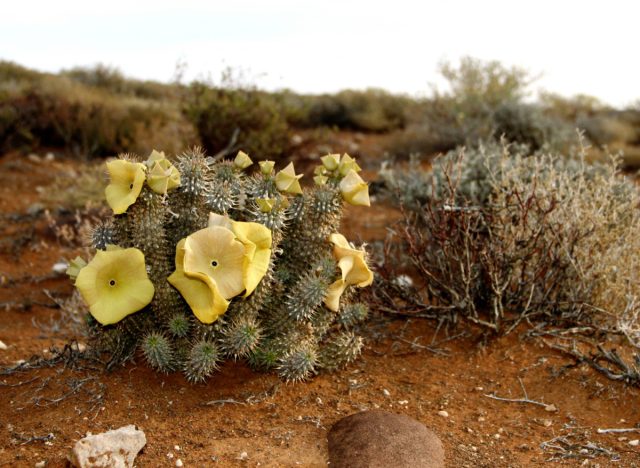

Hoodia is a weight-loss supplement marketed as a natural appetite suppressant, according to research. However, Best tells us, “Hoodia supplements claim to suppress appetite, but there’s insufficient evidence to support this claim. Moreover, the safety and purity of Hoodia products sold online can’t be guaranteed.”
Capsaicin
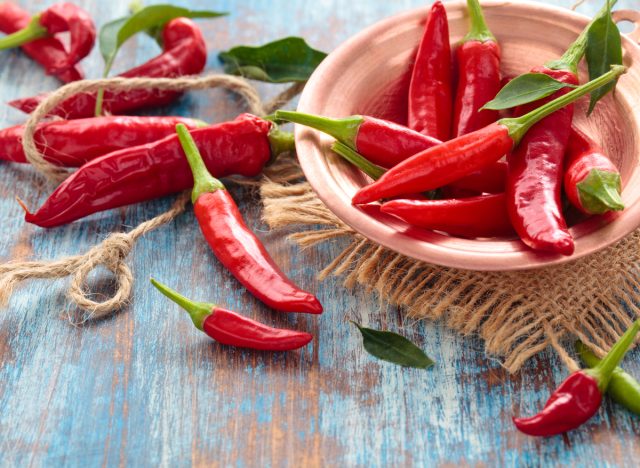

Capsaicin is the compound responsible for the spicy heat in chili peppers. Studies report it can help boost metabolism and even reduce appetite. While some studies suggest it may increase fat burning, more research is needed to confirm its weight-loss benefits.
“Cayenne peppers and chilis contain capsaicin and capsaicinoids, which give them their spicy flavor, and many hold the assertion it can help with weight loss by increasing metabolism and fat burning,” Moody explains. “However, there’s no compelling evidence that capsaicin significantly reduces body fat levels, despite reports that it can have a mild effect on calorie intake.”
Orlistat
This weight-loss supplement is an over-the-counter medication that prevents your body from absorbing dietary fats, research shows. While it can help some people lose weight, it may also cause side effects like diarrhea and abdominal pain.
“Orlistat can have nasty side effects,” cautions Moody. “Having unabsorbed fat passing through your system is unpleasant, especially considering the fat gets exposed to the compounds in your gut, causing them to go rancid. This can result in stomach cramps, foul-smelling bowel movements, more frequent and urgent bowel movements, and headaches.”
Bitter Orange
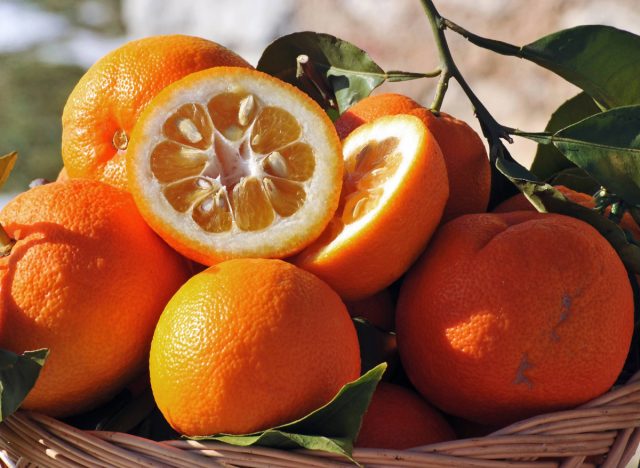

According to the NIH, bitter orange, or Citrus aurantium, is used in weight-loss supplements due to its purported ability to suppress appetite. However, Moody explains while there’s some research supporting these claims, the results have been inconsistent.
Additionally, Moody cautions, “The high doses of bitter orange needed to show significant fat loss may be unsafe. This is especially true considering synephrine (its active ingredient) has been shown to have potentially dangerous effects on blood pressure.”
Chitosan
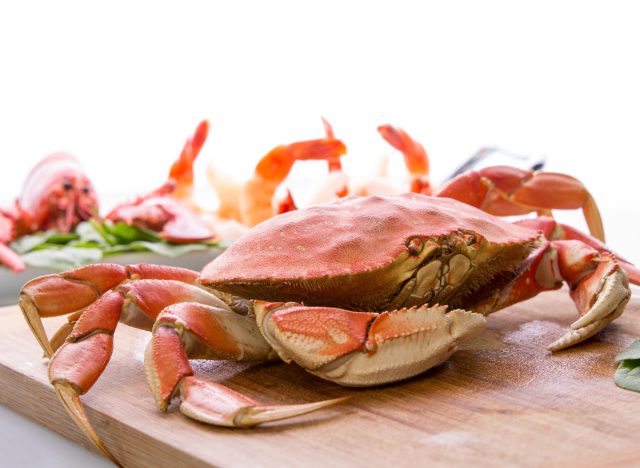

Chitosan is typically marketed as a fat blocker, but scientific evidence supporting its weight-loss claims is limited. Additionally, a recent study in Polymers found that chitosan may cause gastrointestinal side effects such as constipation and bloating.
“Chitosan is derived from chitin, which is found in the shells of crustaceans like crabs and lobster,” Moody explains. “These compounds form a gel in the gut that can bind to fat and prevent absorption. This means the supplement would only work if timed properly around meals, which is not ideal. Additionally, research doesn’t support the fat-blocking mechanism.”
Raspberry Ketones
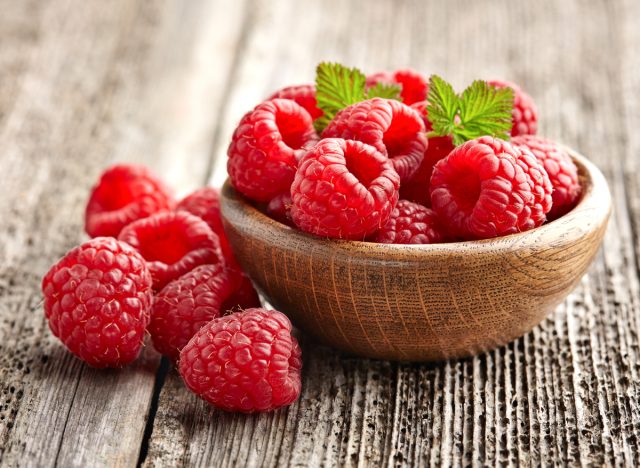

Raspberry ketones, the compounds that provide raspberries with their tantalizing scent, are often championed for their weight-loss benefits. But while some studies claim these ketones can increase fat breakdown and help regulate your metabolism, scientific evidence is lacking.
Moody says, “Not only is this supplement wasteful (it takes two pounds of raspberries to make just one to four milligrams of raspberry ketones), but we have no way of knowing if they’re effective in humans.”
- Source: Dietary Supplements for Weight Loss
- Source: Conjugated Linoleic Acid Effects on Cancer, Obesity, and Atherosclerosis: A Review of Pre-Clinical and Human Trials with Current Perspectives
- Source: Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Its Beneficial Effects in Obesity, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer
- Source: Dietary Supplements for Weight Loss
- Source: Risks Associated with the Use of Garcinia as a Nutritional Complement to Lose Weight
- Source: Garcinia Cambogia Weight-Loss Pill Is No Miracle
- Source: LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury
- Source: Dietary capsaicin and its anti-obesity potency: from mechanism to clinical implications
- Source: Orlistat
- Source: Bitter Orange
- Source: Anti-Obesity Effects of Chitosan and Its Derivatives
- Source: Pharmacological Exploration of Phenolic Compound: Raspberry Ketone—Update 2020









