The #1 Best Oil To Cook With While Watching Your Cholesterol
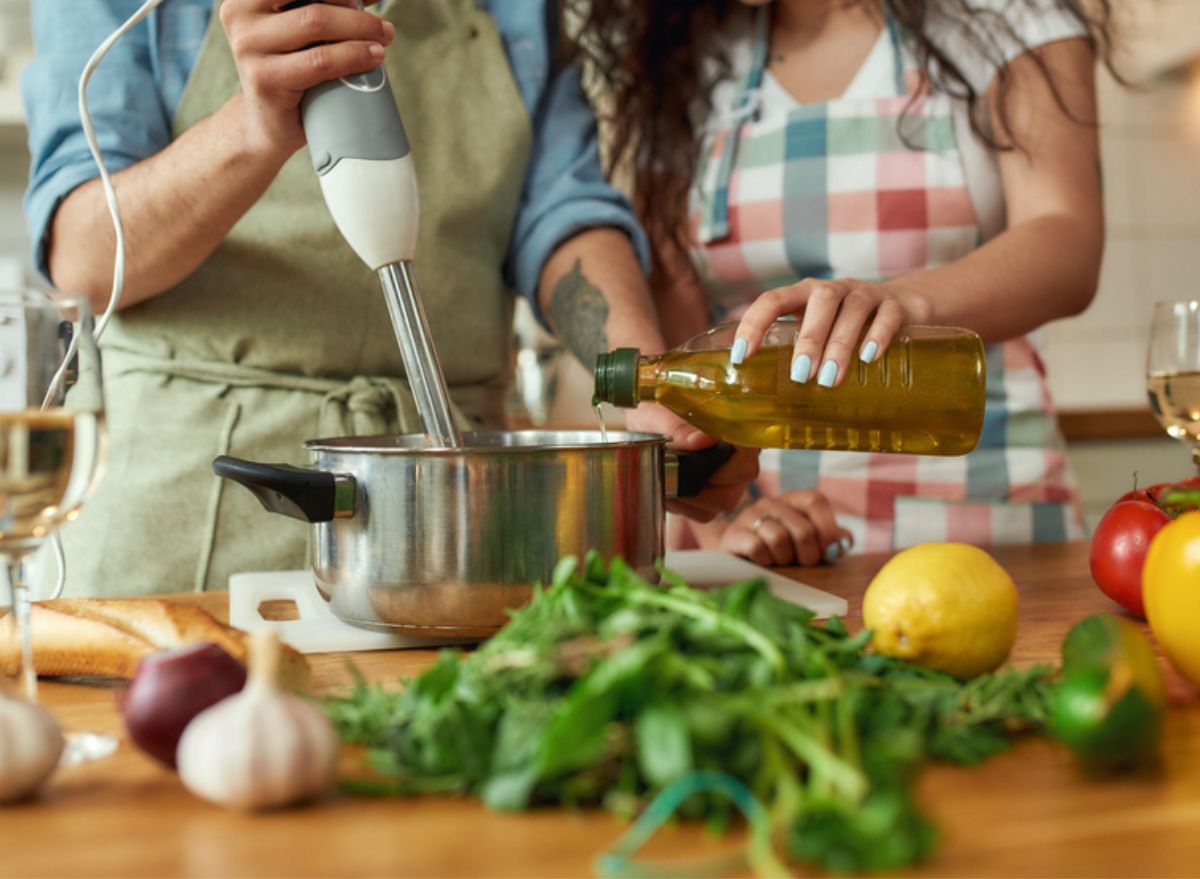

To keep you your cholesterol levels in check, and improve your overall heart health, I recommend making olive oil your go-to oil for not only salad dressings and finishing food but also for your primary oil for cooking.
My pantry is always well stocked with a variety of olive oils, including extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO), light olive oil, and olive oil infused with lemon, garlic, or herbs. Depending on what I’m cooking, the type of olive oil with change. But regardless of the specific type of olive oil I cook with, all are great while watching your cholesterol.
Many health-conscious home cooks think they should be cooking with a vegetable oil high in unsaturated fat like soybean, canola, corn, or peanut oil. These oils are often thought of as being more versatile for cooking and stable at high temperatures. And because they are primarily unsaturated fats, they’re also considered by many to be a healthy option.
However, any recipe that calls for a vegetable oil can also be made with olive oil, even including fried foods and baked goods. (Although fried foods and baked goods are not the best choices for achieving a healthy blood cholesterol level.) Professional chefs often prefer to use EVOO because they consider it a flavor enhancer.
What is olive oil, and why is it the best oil for cholesterol?

People often ask me about what exactly olive oil is and how it’s made. Simply put, olive oil is the “juice of an olive.” Olive oil comes from the fleshy part of the olives, not the seeds. Mechanical pressing is the most common way olive oil is processed and bottled.
There are several types of olive oils that are classified as refined or unrefined. EVOO is unrefined and will have the most health benefits, thanks to its phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity, and other bioactive components. Refined olive oil is labeled as either “olive oil” or “light” olive oil or “light-tasting” olive oil. These products are often a blend of EVOO with refined olive oil. They impart a more neutral flavor, making these types of olive oil great for baking or other cooking applications where you want a lighter flavor.
Health-wise, all olive oils have the same number of calories and beneficial fatty acid profile. EVOO olive oil will have more polyphenols and antioxidants, which are what give olive oils their flavor but also provide additional health benefits. There are more than 1,400 published, peer-review articles about the links between olive oil and improved cardiovascular health.
One of the most robust studies, PREDIMED reported that individuals with higher olive oil consumption showed a 48% lower risk of cardiovascular disease than those with the lowest olive oil intake. What’s more, for each 10 gram per time spent being physically active increase in extra-virgin olive oil consumption, cardiovascular disease decreased by 10%, respectively. No significant associations were found between cancer and all-cause mortality. Additionally, several recent studies suggest that EVOO may provide additional cholesterol benefits by increasing beneficial HDL cholesterol levels, due to the higher phenolic compounds in EVOO.
RELATED: This is the #1 Biggest Cholesterol Mistake You Can Make
Cooking with olive oil
Olive oil can be used as a great substitute for vegetable oils in most recipes. The benefit of olive oil is that significant scientific agreement suggests that olive oil can help maintain a healthy heart to reduce the risk of heart disease. Olive oil is exceptionally high in monounsaturated fat and has lower levels of polyunsaturated fat compared to other vegetable oils.
If you require neutral oil for your recipe, go with olive oil or light-tasting olive oil. These oils won’t change the flavor of your food. But we recommend experimenting with extra virgin olive oil as a substitute for vegetable oil. The smoke point for refined olive oil is 468°F, which is considered high enough for any type of cooking. The smoke point for EVOO oil smoke point ranges between 350-410°F, slightly lower but still high enough for high-temp cooking.
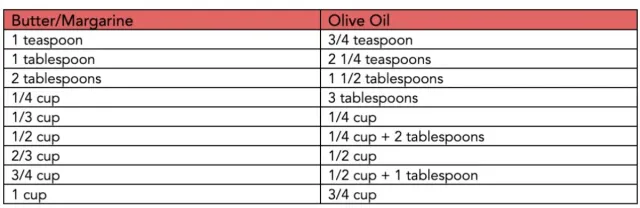
For the most part, you can use olive oil as a 1:1 replacement for a vegetable oil. But when it comes to using olive oil in place of margarine or butter in recipes, you will generally want to reduce the amount of olive oil. This will work for most cooking applications like sautéing or making sauces but test it out in your baked goods until you get the right ratio.
3 tips for choosing the olive oil right for your needs
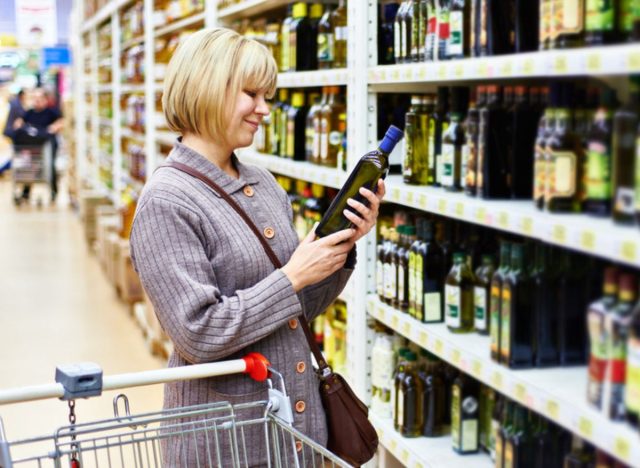

Here are three great tips for choosing high-quality olive oil.
Check the best-by date.
Olive oil is best when it is first produced, but it should retain its goodness for about two years from bottling, depending on how the oil has been handled. On the bottle, look for the best if used by date on the bottle.
Buy enough for a few months.
Olive oil is a natural product like produce and it will degrade when exposed to heat, oxygen, and light. Check the bottles of oil you have now and be sure you have oil well within the best-by date.
Look for quality assurance seals.
The bottle may carry an origin seal that indicates the region of origin, or certification seals such as the NAOOA Quality Seal, which indicates the brand has agreed to join a program that involves random off-the-shelf testing for compliance with the widely held international standards of purity and quality.









